Earwax, the natural protector of our ears, serves a vital role in maintaining the health of the delicate ear canal. However, when it overstays its welcome, issues can arise. Impacted earwax, a more prevalent problem than many realize, impacts up to 6% of individuals, according to a survey.
Impacted earwax, also known as cerumen impaction, potentially causes jaw pain. You can feel jaw pain on one side by ear, or on both sides, depending upon the root cause. If you sense a buildup in your ears, be vigilant for potential jaw discomfort.
Ear Wax Origins & Factors Behind Blockages
Earwax, also known as cerumen, is produced by specialized glands called ceruminous glands located in the ear canal. These glands secrete a waxy substance that serves several essential functions.
Earwax helps keep the delicate skin of the ear canal moisturized and prevents it from becoming dry and itchy. It acts as a protective barrier, trapping dust, debris, and foreign particles before they reach the eardrum. As the jaw moves during talking or chewing, earwax gradually migrates from the deeper parts of the ear canal toward the outer opening, carrying away dirt and dead skin cells.
Factors Contributing to Earwax Buildup and Blockages
While earwax is a natural and necessary substance, certain factors can lead to excessive buildup or blockages:
- Genetic Factors and Hormonal Changes:
Some individuals naturally produce more earwax due to genetic variations. Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy, can also influence ceruminous gland activity.
- Inadequate Ear Hygiene Practices:
Improper cleaning techniques, such as using cotton swabs or inserting foreign objects into the ear canal, can push earwax deeper and compact it. Frequent use of earplugs or earbuds can also disrupt the natural self-cleaning process.
- Aging-Related Changes:
As we age, the consistency of earwax may change. It can become drier and harder, making it more likely to cause blockages. Reduced jaw movement in older adults may hinder the natural migration of earwax.
- Use of Hearing Aids or Earbuds:
Devices like hearing aids or earbuds can inadvertently push earwax deeper into the ear canal. Regular cleaning and maintenance of these devices are essential to prevent buildup.
- Skin Conditions and Anatomical Abnormalities:
Certain skin conditions (e.g., eczema) can affect the ear canal’s lining, leading to excessive earwax production. Anatomical variations, such as a narrow or curved ear canal, may make it easier for earwax to accumulate.
While earwax is generally harmless, excessive buildup can cause discomfort, hearing impairment, or even ear infections. If you experience symptoms like ear pain, fullness, or decreased hearing, consult a healthcare professional for safe and effective earwax removal.
Symptoms of Jaw Pain Caused by Impacted Earwax
When earwax becomes impacted, it can lead to various symptoms, including jaw pain. Here are the common signs associated with jaw discomfort caused by impacted earwax:
Dull or Aching Pain in the Jaw Joint or Surrounding Muscles:
Impacted earwax can put pressure on the surrounding tissues, including the jaw joint (temporomandibular joint or TMJ) and the muscles around it. This pressure may result in a persistent, dull, or aching pain in the jaw area.
Difficulty Opening or Closing the Mouth Fully:
The presence of excessive earwax can interfere with the normal movement of the jaw.
Individuals may experience limitations in fully opening or closing their mouths due to discomfort or stiffness.
Clicking or Popping Sounds When Chewing or Moving the Jaw:
Impacted earwax can alter the alignment of the jaw joint or affect its movement.
As a result, you may notice clicking, popping, or grating sounds when you chew, speak, or move your jaw.
Ear Pain When Swallowing:
Sometimes, earwax buildup can extend to the throat area, causing referred pain. Swallowing may exacerbate the discomfort, leading to ear pain. Explore the reasons why the ear hurt when swallowing and how to get rid of this discomfort.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek professional advice. A healthcare provider can assess your condition, perform safe earwax removal if necessary, and provide relief from jaw pain. Remember to avoid inserting objects into your ears, as this can worsen the situation.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
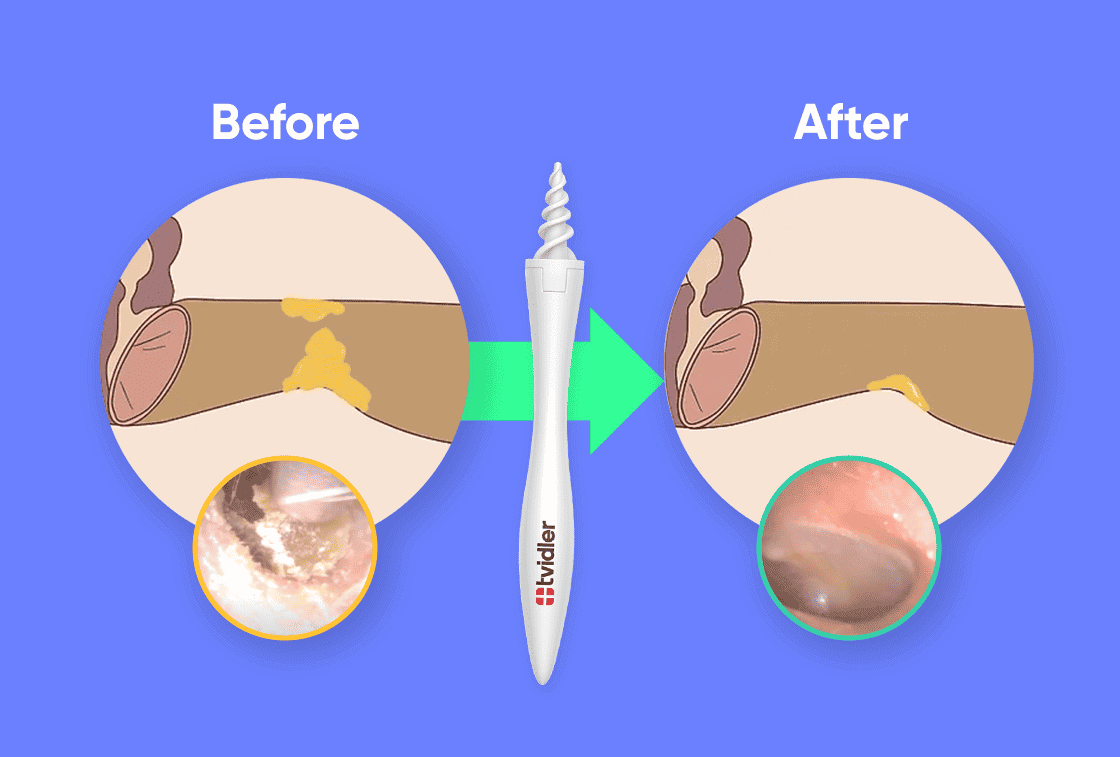
Your healthcare provider can assess earwax blockage by performing a physical examination. They will use an otoscope, a special tool that illuminates and magnifies the inner ear, to inspect the ear canal. The otoscope allows visualization of the eardrum and any cerumen impaction that might be obstructing it.
Treatment focuses on clearing the blockage and relieving jaw discomfort. Here are some treatment options for earwax impaction:
1. Earwax Softening Drops or Irrigation
Medicated ear drops containing ingredients like carbamide peroxide can help soften the wax. These drops facilitate easier removal by a healthcare provider or self-cleaning. Use them as directed, as prolonged use can cause irritation.
Irrigation systems are also effective. They involve flushing the ear with warm water and saline or diluted hydrogen peroxide. Avoid using cold water, as it may cause vertigo or dizziness.
2. Manual Removal by a Healthcare Professional
A small, curved tool called a curette can be used to gently scoop out excess wax.
If earwax buildup persists, regular professional cleaning (once or twice a year) may be necessary.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
To prevent recurrence, consider using earwax-softening agents like saline, mineral oil, or olive oil at home. Follow safe practices to reduce wax buildup, as advised by your healthcare provider.
Avoid inserting objects (like cotton swabs or paper clips) into your ears, as they can worsen the situation. For manual cleaning with safe tools, explore our roundup of the top ear wax removal tools.
Try Ear Wax Removal Tool
Consider trying the Tvidler Pro Ear Wax Removal Tool for a hassle-free and effective ear cleaning experience. With its patented rotating mechanism, it gently eliminates ear wax, grime, and debris without causing any discomfort. Crafted from premium-grade plastic, it boasts an ergonomic design for easy handling.
The Tvidler Pro features medical-grade silicone tips, ensuring both safety and efficacy. This user-friendly tool provides a hygienic solution for maintaining optimal ear health and promoting clear hearing. If you’re looking for a convenient and reliable ear wax removal option, the Tvidler Pro is definitely worth considering. Check out our Tvidler Pro review to learn more about its benefits firsthand.
Earwax Blockage Prevention Strategies
Here are some earwax blockage prevention strategies to maintain healthy ears and minimize the risk of jaw pain:
- Avoid Cotton Swabs and Objects:
Cotton swabs can push earwax deeper into the canal and lead to blockages. Refrain from inserting any other objects (like bobby pins or paper clips) into your ears. Let your ears handle their own cleaning.
- Regular Ear Hygiene Monitoring:
Keep an eye on your ear hygiene. If you notice excessive wax buildup, seek professional cleaning. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help prevent major blockages.
- Follow Proper Earwax Removal Techniques:
Follow the recommended techniques for earwax removal. These may include using earwax-softening drops, warm water irrigation, or professional manual removal using a safe and effective earwax removal tool such as Tvidler.
Remember, maintaining good ear health contributes to overall well-being. And while you’re at it, consider some jaw exercises and a gentle ear massage for ear wax dislodging to keep everything in balance!